E-Waste Handling Mastery: A Business Owner’s Complete Guide to Managing Electronic Waste Responsibly
Last month, a mid-sized manufacturing company in Ohio thought they were being environmentally responsible when they donated 200 old computers to a local school district. What they didn’t realize was that 30% of those devices contained recoverable client data, and several hard drives still held proprietary manufacturing processes. Six weeks later, when a competitor launched a product suspiciously similar to their latest innovation, they discovered their “charitable donation” had become a corporate espionage goldmine.
This cautionary tale illustrates a critical reality facing businesses today: electronic waste isn’t just an environmental concern—it’s a security, compliance, and competitive issue that demands sophisticated e-waste handling strategies. With the average business generating over 40 pounds of electronic waste per employee annually, the days of simply tossing old equipment in the dumpster or making well-intentioned donations are long gone.
Managing e-waste effectively requires understanding complex regulations, implementing secure processes, and working with qualified partners who can navigate the intricate landscape of electronic waste disposal. It’s about protecting sensitive data, maintaining regulatory compliance, optimizing costs, and contributing to environmental sustainability—all while keeping your business operations running smoothly.
Whether you’re dealing with a handful of outdated laptops or managing the disposal of an entire data center, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies needed to handle electronic waste responsibly and profitably. You’ll discover how proper e-waste management can transform a potential liability into a competitive advantage while protecting your organization from costly mistakes.
The stakes are higher than ever, and the time for reactive approaches to electronic waste has passed. Let’s explore how to build a proactive, comprehensive e-waste handling strategy that protects your business and contributes to a more sustainable future.
The Hidden Crisis of Business E-Waste
The numbers surrounding electronic waste generation are staggering and growing exponentially. Globally, we generate over 50 million metric tons of e-waste annually, with businesses contributing approximately 60% of this total. In the United States alone, commercial and institutional sectors dispose of more than 3 million tons of electronic equipment each year, and this figure increases by 8-10% annually as technology refresh cycles accelerate.
What makes these statistics particularly alarming is the composition of electronic waste. Modern devices contain over 60 different elements from the periodic table, including precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum, rare earth elements critical to technology manufacturing, and toxic substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium that pose serious environmental and health risks when improperly disposed of.
The environmental impact of poor e-waste handling extends far beyond simple landfill concerns. When electronic devices end up in standard waste streams, toxic materials can leach into groundwater systems, contaminating drinking water supplies for entire communities. Improper incineration releases dangerous toxins into the air, contributing to respiratory problems and environmental degradation. Perhaps most troubling, much of the world’s e-waste ends up in developing countries, where informal recycling operations expose workers and communities to dangerous chemicals while providing minimal material recovery.
For businesses, the implications go beyond environmental responsibility. Poor e-waste handling represents a massive missed economic opportunity. The materials contained in discarded electronics are worth an estimated $57 billion annually, yet less than 20% of global e-waste is properly recycled and recovered. Companies that fail to implement effective e-waste handling strategies are literally throwing money away while exposing themselves to significant regulatory and reputational risks.
The regulatory environment is tightening rapidly, with new laws being enacted regularly that impose strict requirements on business e-waste handling. Violation penalties can range from thousands to millions of dollars, and regulatory agencies are becoming increasingly aggressive in enforcement. More concerning for many businesses is the reputational damage that can result from poor environmental practices, as consumers and business partners increasingly evaluate companies based on their sustainability commitments and actual performance.
Understanding E-Waste Categories and Handling Requirements
Effective managing e-waste begins with understanding that not all electronic waste is created equal. Different types of equipment require different handling approaches, security protocols, and disposal methods. Developing this understanding is crucial for implementing appropriate e-waste handling procedures that protect both your business and the environment.
Computer equipment and servers represent the most common category of business e-waste, but also potentially the most problematic from a security standpoint. Desktop computers, laptops, and servers typically contain hard drives or solid-state drives that store vast amounts of sensitive information. Even after standard deletion procedures, sophisticated data recovery techniques can often retrieve confidential information, making proper data destruction a critical component of e-waste handling for these devices.
Server equipment presents additional challenges due to its complexity and the sensitive nature of the data it typically contains. Many servers contain multiple storage devices, redundant systems, and backup components that can retain data even after primary systems are wiped. Network equipment like routers, switches, and firewalls often cache data and may contain configuration information that could compromise network security if not properly handled during disposal.
Mobile devices and tablets have become increasingly problematic for e-waste management as their prevalence in business environments has exploded. These devices often contain corporate email, customer contact information, and access credentials for business systems. The integration of mobile devices with cloud services and corporate networks means that improper disposal can provide access to far more than just the data stored locally on the device.
Wearable technology adds another layer of complexity, as these devices may contain biometric data, location tracking information, and health-related data that could be subject to specific privacy regulations. Battery handling for mobile devices also requires special consideration, as lithium-ion batteries can be dangerous if damaged and require specialized recycling processes.
Peripheral equipment like printers, scanners, and multifunction devices present often-overlooked security risks. Many modern printers contain hard drives that store copies of every document printed, scanned, or copied. These devices can become treasure troves of sensitive information if not properly handled during disposal. Similarly, audio-visual equipment may contain stored presentations, recordings, or configuration data that could be valuable to competitors or malicious actors.
Specialized electronic equipment requires industry-specific e-waste handling approaches. Medical devices must be handled in compliance with HIPAA regulations and may contain patient data that requires specific destruction procedures. Industrial control systems may contain proprietary process information or security configurations that could compromise operational security if improperly disposed of. Telecommunications equipment often contains customer data and network configuration information that requires careful handling to protect both privacy and security.
Regulatory Landscape for E-Waste Management
The regulatory environment governing e-waste handling is complex, multi-layered, and constantly evolving. Understanding these requirements is essential for developing compliant e-waste management strategies that protect your business from costly violations and penalties.
At the federal level, the Environmental Protection Agency provides guidelines for e-waste handling under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), which governs the disposal of hazardous waste. While most business electronics don’t qualify as hazardous waste under RCRA, certain components—particularly cathode ray tube monitors and devices containing mercury—may be subject to hazardous waste regulations that require specialized handling and disposal procedures.
The EPA’s Responsible Recycling (R2) standard provides a framework for responsible e-waste handling that many businesses use as a baseline for their programs. This standard emphasizes data security, worker safety, and environmental protection throughout the recycling process. While compliance with R2 isn’t legally required, many insurance companies and business partners now expect their vendors to work with R2-certified recyclers.
OSHA regulations also impact e-waste handling, particularly regarding worker safety during equipment handling and transportation. Businesses must ensure that employees involved in e-waste collection, storage, and preparation for disposal are properly trained and protected from potential hazards like sharp edges, heavy lifting injuries, and exposure to potentially toxic materials.
State-level regulations vary significantly and are becoming increasingly stringent. Many states have implemented Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs that require manufacturers to take responsibility for the end-of-life disposal of their products. These programs often include specific requirements for businesses regarding how they can dispose of certain types of electronic equipment.
California’s Electronic Waste Recycling Act is among the most comprehensive state-level regulations, requiring businesses to work with certified recyclers and prohibiting the disposal of certain electronic devices in standard waste streams. New York’s Electronic Equipment Recycling and Reuse Act imposes similar requirements and includes specific provisions for data destruction that businesses must follow.
Interstate transportation of e-waste is governed by Department of Transportation regulations when equipment contains hazardous materials. Businesses that ship e-waste to recycling facilities in other states must ensure compliance with hazardous materials transportation requirements, which can include special packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements.
Industry-specific regulations add additional layers of complexity for managing e-waste. Healthcare organizations must ensure that any electronic equipment disposal complies with HIPAA requirements for protecting patient health information. Financial services companies must meet specific data protection requirements under regulations like Gramm-Leach-Bliley and various state privacy laws. Government contractors may be subject to additional security requirements that impact how they can dispose of electronic equipment.
International considerations become important for businesses that operate globally or work with international partners. The Basel Convention governs international trade in hazardous waste and can impact how businesses handle e-waste that contains certain materials. Export restrictions may prevent certain types of e-waste from being shipped to some countries for recycling, requiring domestic disposal solutions.
Developing an Effective E-Waste Management Strategy
Creating a comprehensive e-waste management strategy requires systematic planning, stakeholder engagement, and ongoing commitment to continuous improvement. The most successful programs treat e-waste handling as a strategic business function rather than a simple operational task.
The foundation of effective managing e-waste begins with a thorough assessment of your current situation. Conduct a comprehensive e-waste audit to identify all sources of electronic waste within your organization, estimate current and future volumes, and assess the types of equipment and associated risks involved. This audit should include not just obvious items like computers and printers, but also embedded systems, telecommunications equipment, and any electronic devices that could contain sensitive information.
Volume estimation and forecasting are critical for budget planning and vendor selection. Analyze your equipment refresh cycles, growth projections, and technology roadmaps to predict future e-waste generation. Consider seasonal variations, major system upgrades, and business expansion plans that could significantly impact e-waste volumes. This forecasting will help you negotiate better contracts with service providers and ensure adequate capacity for peak disposal periods.
Risk assessment should evaluate both security and compliance risks associated with different types of equipment and data. Classify your electronic equipment based on the sensitivity of the data it contains, regulatory requirements that apply to its disposal, and potential security implications of improper handling. This classification system will drive decisions about appropriate handling procedures, security requirements, and vendor selection criteria.
Policy development creates the framework for consistent, compliant e-waste handling across your organization. Your e-waste policy should clearly define roles and responsibilities, establish procedures for different types of equipment, specify security requirements and data handling protocols, outline vendor selection and management criteria, and provide guidelines for staff training and awareness.
The policy should be integrated with your broader information security, environmental, and procurement policies to ensure consistency and avoid conflicts. Regular policy reviews and updates are essential as regulations change and your business evolves.
Implementation requires careful planning and phased rollout to minimize disruption to business operations. Start with pilot programs in specific departments or locations to test procedures and identify potential issues before organization-wide deployment. Develop comprehensive training programs for all staff involved in e-waste handling, from initial identification and collection through final disposal documentation.
Monitoring and measurement systems provide the data needed to evaluate program effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. Establish key performance indicators that track volume handled, cost per unit, compliance metrics, security incidents, and environmental impact measures. Regular reporting and analysis of these metrics will help you optimize your program over time and demonstrate value to stakeholders.
Best Practices for Managing E-Waste Throughout the Lifecycle
The most effective e-waste handling strategies take a lifecycle approach that considers electronic waste implications from procurement through final disposal. This comprehensive perspective can significantly reduce waste volumes, improve cost efficiency, and minimize environmental impact while maintaining security and compliance.
Procurement decisions have enormous impact on future e-waste handling requirements. When evaluating new equipment purchases, consider the manufacturer’s take-back programs, the repairability and upgradeability of the equipment, energy efficiency and environmental certifications, end-of-life disposal requirements and costs, and security features that facilitate data destruction.
Establishing vendor requirements for sustainability and end-of-life support can simplify future e-waste handling while supporting your environmental goals. Some manufacturers offer comprehensive take-back programs that can significantly reduce the complexity and cost of equipment disposal when it reaches end-of-life.
During the use phase, proper maintenance and lifecycle management can extend equipment life and reduce waste generation. Implement preventive maintenance programs to maximize equipment lifespan, regularly evaluate upgrade versus replacement decisions based on total cost of ownership, and optimize energy efficiency to reduce environmental impact throughout the equipment lifecycle.
Strategic refresh planning can help minimize waste and optimize value recovery. Rather than reactive replacement when equipment fails, plan refresh cycles based on business requirements, technology evolution, and cost optimization. This approach allows for better planning of disposal activities and can improve asset recovery through resale or donation programs.
End-of-life preparation is crucial for secure and efficient e-waste handling. Develop systematic procedures for data backup and migration to ensure business continuity while preparing for equipment disposal. Implement comprehensive asset inventory and documentation systems that track equipment from procurement through disposal, including all security and compliance requirements.
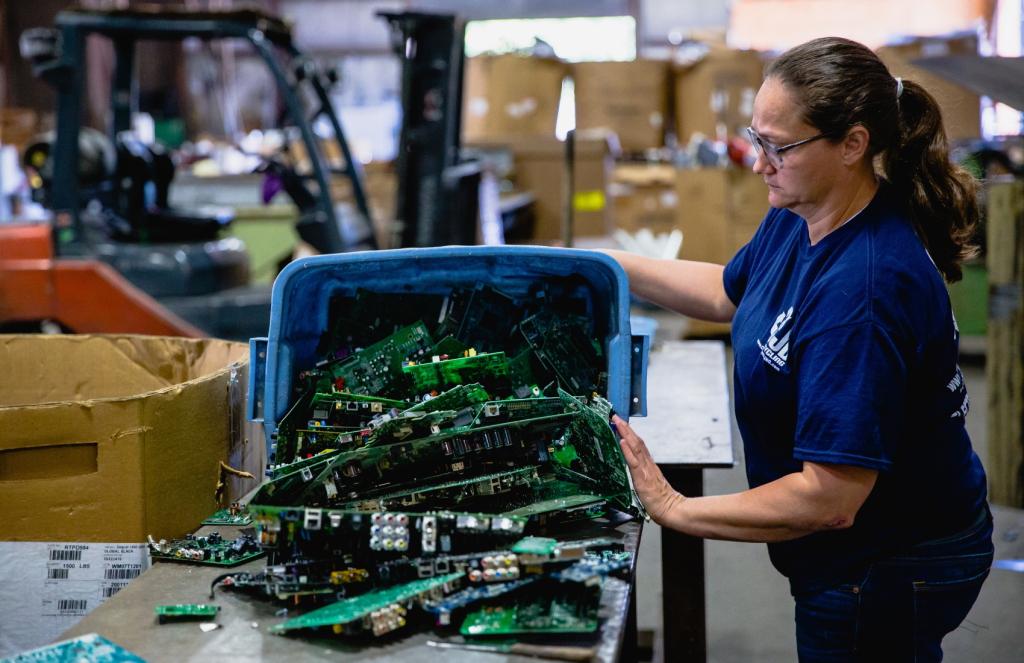
Secure storage protocols protect your business during the transition from active use to final disposal. Equipment awaiting disposal should be stored in secure areas with access controls and environmental protection. Clear chain of custody documentation should begin as soon as equipment is designated for disposal and continue through final processing.
The disposal and recycling phase requires careful partner selection and ongoing management to ensure security, compliance, and environmental protection. Work with certified recyclers who can demonstrate appropriate capabilities and maintain comprehensive documentation throughout the process. Regular audits of recycling partners help ensure ongoing compliance and performance.
Technology Solutions for E-Waste Tracking and Management
Modern technology solutions can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of e-waste handling while reducing costs and improving compliance. The key is selecting and implementing systems that integrate well with your existing business processes and provide actionable insights for continuous improvement.
Asset management systems provide the foundation for effective e-waste tracking by maintaining comprehensive records of equipment throughout its lifecycle. RFID and barcode tracking technologies enable automated data collection and real-time visibility into equipment status and location. These systems can automatically trigger e-waste handling processes when equipment reaches predetermined age or condition thresholds.
Cloud-based inventory management platforms offer scalability and accessibility advantages, particularly for businesses with multiple locations or remote operations. These systems can integrate with procurement and financial systems to provide comprehensive lifecycle cost analysis and support data-driven decision making about equipment refresh and disposal timing.
Automated reporting capabilities can significantly reduce the administrative burden of e-waste management while improving compliance and performance monitoring. Modern systems can generate compliance reports, track vendor performance metrics, calculate environmental impact measures, and provide cost analysis and optimization recommendations.
Data analytics and reporting tools help identify trends and opportunities for improvement in e-waste handling processes. Predictive analytics can forecast future e-waste volumes based on historical patterns and business growth projections. Performance dashboards provide real-time visibility into key metrics and can alert managers to potential issues before they become problems.
Integration with existing business systems maximizes the value of technology investments while minimizing disruption to established processes. ERP system connectivity enables seamless data flow between asset management, procurement, and financial systems. This integration can automate many e-waste handling processes while providing comprehensive visibility and control.
Mobile applications can streamline field operations for e-waste collection and processing. These tools enable real-time data collection, photo documentation, and digital signatures for chain of custody tracking. Mobile capabilities are particularly valuable for businesses with multiple locations or field service operations.
Cost Management and Financial Optimization
Understanding and optimizing the costs associated with e-waste handling requires a comprehensive view that considers both direct expenses and hidden costs, as well as opportunities for revenue generation and cost avoidance.
Direct costs are the most visible component of e-waste handling expenses and include service provider fees for collection, processing, and disposal, transportation and logistics costs for moving equipment to recycling facilities, and documentation and compliance expenses for required reporting and certifications.
These costs can be optimized through volume consolidation, negotiated contract terms, and strategic timing of disposal activities. Many recyclers offer volume discounts or preferred pricing for consistent, predictable volumes. Coordinating disposal activities across multiple locations or departments can help achieve these volume thresholds.
Hidden costs often exceed direct expenses but are less visible in traditional accounting systems. Risk mitigation value represents the insurance effect of proper e-waste handling against potential fines, security breaches, and environmental liabilities. While difficult to quantify precisely, this protection can be worth many times the direct cost of proper disposal.
Staff time and resource allocation represent significant hidden costs that are often overlooked. Internal handling of e-waste disposal typically requires more employee hours than anticipated, taking valuable staff away from revenue-generating activities. Professional e-waste handling services often provide better value when these opportunity costs are properly considered.
Revenue generation opportunities can offset disposal costs and sometimes generate positive returns on e-waste handling investments. Asset recovery programs can recover value from functional equipment through resale, donation, or component harvesting. Even non-functional equipment contains valuable materials like precious metals that can be recovered and credited to your account.
Tax incentive optimization provides additional financial benefits through proper documentation and strategic disposal timing. Equipment donations to qualified organizations can generate substantial tax deductions, while proper depreciation and disposal documentation supports accurate financial reporting and tax planning.
Some businesses have discovered that systematic e-waste handling can become a profit center through comprehensive asset recovery programs. By working with recyclers who offer competitive asset recovery pricing and implementing systems to identify equipment suitable for resale or refurbishment, organizations can generate revenue that exceeds disposal costs.
Choosing and Working with E-Waste Management Partners
The success of your e-waste handling program depends heavily on the quality and reliability of your service providers. Selecting the right partners requires careful evaluation of capabilities, compliance, and cultural fit with your organization’s values and requirements.
Vendor evaluation should begin with verification of appropriate certifications and compliance credentials. Look for R2 (Responsible Recycling) certification, which ensures adherence to strict standards for data security, worker safety, and environmental protection. e-Stewards certification provides even higher standards and prohibits the export of toxic materials to developing countries.
ISO certifications, particularly ISO 14001 (environmental management) and ISO 27001 (information security), demonstrate systematic approaches to critical business processes. Industry-specific certifications may be required depending on your business sector and regulatory requirements.
Service capability assessment should evaluate the provider’s ability to handle your specific volume requirements, equipment types, and service level expectations. Geographic coverage is important for multi-location businesses, and emergency response capabilities can be crucial for urgent disposal needs.
Financial stability and insurance coverage protect your business from vendor performance issues or liability exposure. Request financial references and verify appropriate insurance coverage for data breach, environmental liability, and general business operations.
Developing comprehensive service level agreements ensures clear expectations and accountability for all aspects of the e-waste handling relationship. These agreements should specify performance standards and metrics, reporting and documentation requirements, security and compliance protocols, pricing and billing procedures, and emergency response capabilities.
Regular performance monitoring and relationship management help ensure ongoing value and compliance from your e-waste handling partners. Conduct periodic audits of vendor facilities and processes, review performance metrics and compliance reports, and maintain open communication about changing requirements or improvement opportunities.
Building long-term partnerships with qualified providers often delivers better value than transaction-based relationships. Established partners develop deeper understanding of your business requirements and can often provide more competitive pricing and enhanced service levels for reliable, ongoing business.
Future Trends and Emerging Challenges
The e-waste handling landscape continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancement, regulatory development, and changing business practices. Understanding these trends can help you anticipate future requirements and position your organization for success in managing e-waste challenges.
Technology evolution is creating new categories of electronic waste while changing the characteristics of traditional equipment. The proliferation of IoT devices means businesses are dealing with vastly more electronic devices than in the past, each potentially containing sensitive data or proprietary information. These devices often have limited lifespans and may be difficult to service or upgrade, leading to higher disposal volumes.
Cloud computing is changing equipment refresh patterns and disposal volumes as businesses shift from on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based services. While this trend may reduce some traditional e-waste categories like servers and networking equipment, it’s also driving increased demand for mobile devices and edge computing equipment that present different disposal challenges.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications are being integrated into e-waste handling processes, improving sorting efficiency and material recovery rates. These technologies can also enhance data destruction verification and provide better tracking and documentation of disposal activities.
The regulatory environment continues to tighten, with new requirements being implemented regularly at federal, state, and local levels. Extended Producer Responsibility programs are expanding to cover more types of equipment and impose greater obligations on businesses. International harmonization efforts may standardize some requirements but could also introduce new compliance complexities for global businesses.
Privacy regulations are becoming more stringent and comprehensive, with implications for how businesses must handle data destruction during e-waste disposal. The trend toward more expansive definitions of personal and sensitive data means more types of equipment may require specialized handling and documentation.
Industry innovation is focused on developing more sustainable and efficient approaches to managing e-waste. Circular economy principles are driving demand for equipment designed for easier repair, upgrade, and recycling. Advanced recycling technologies are improving material recovery rates and enabling recycling of previously difficult materials.
Blockchain technology is being explored for creating tamper-proof documentation of e-waste handling and disposal activities. This could significantly enhance compliance reporting and provide greater assurance of proper handling throughout the disposal process.
Taking Control of Your E-Waste Future
The complexity and importance of proper e-waste handling will only continue to grow as technology becomes more integral to business operations and regulatory requirements become more stringent. The organizations that thrive will be those that treat managing e-waste as a strategic capability rather than a necessary burden.
Success in e-waste handling requires leadership commitment to sustainable practices, systematic approaches that integrate with broader business processes, and ongoing investment in continuous improvement. The most effective programs view e-waste management as an opportunity to demonstrate environmental leadership, optimize costs, and strengthen security rather than simply a compliance requirement.
Getting started doesn’t require perfect knowledge or comprehensive systems—it requires commitment to improvement and willingness to learn. Begin with a thorough assessment of your current situation and immediate risks. Identify quick wins that can provide immediate value while building momentum for more comprehensive improvements.
Develop a realistic implementation timeline that balances urgency with practical constraints. Focus on building strong partnerships with qualified service providers who can provide expertise and support as your program matures. Invest in staff training and awareness to ensure consistent execution of your e-waste handling procedures.
The investment in proper e-waste handling pays dividends through reduced risk exposure, cost optimization, and competitive advantages from demonstrated environmental leadership. More importantly, it contributes to a more sustainable future while protecting your business from the growing costs and risks of poor electronic waste management.
For businesses ready to implement comprehensive e-waste handling solutions, CJD E-Cycling provides expert guidance and services designed to meet the unique needs of organizations across all industries. With proven processes, appropriate certifications, and a commitment to security and environmental responsibility, professional e-waste management services provide the expertise and peace of mind your business needs.
Don’t wait for a crisis to force action on e-waste handling. The businesses that succeed will be those that proactively address these challenges with comprehensive strategies and qualified partners. Take control of your e-waste future today by implementing the practices and partnerships that will protect your business and contribute to environmental sustainability for years to come.
The choice is yours: you can either invest in proper e-waste handling now, or potentially pay much more later through fines, security breaches, and missed opportunities. The smart approach is to be proactive, and the time to start is now.
For comprehensive e-waste management solutions that protect your business while supporting environmental sustainability, CJD E-Cycling offers the expertise and services you need to succeed in today’s complex electronic waste landscape.