In today’s digital workplace, the average office employee uses 1.5 electronic devices daily, contributing to the staggering 50 million tons of business e-waste generated globally each year. For Metro East companies, managing this electronic waste isn’t just an environmental consideration—it’s a legal necessity. Illinois banned e-waste from landfills years ago, making proper disposal mandatory for businesses of all sizes.
But beyond compliance, smart business e-waste management creates opportunities for cost savings, enhanced security, and demonstrable corporate responsibility. Whether you’re drowning in outdated laptops or planning your next IT refresh, implementing a structured approach to e-waste can transform a business liability into an operational advantage.
This guide will walk Metro East businesses through creating an effective e-waste management program that meets compliance requirements while delivering tangible benefits to your bottom line and the environment.
Understanding Business E-Waste Challenges
Business e-waste encompasses a broad spectrum of items including:
- Desktop computers, laptops, and servers
- Monitors, printers, and peripherals
- Mobile phones and tablets
- Networking equipment
- Office electronics (projectors, copiers, etc.)
- Specialized industry equipment with electronic components
Metro East businesses face several distinct challenges when dealing with these materials:
Volume Management: Unlike residential e-waste, business electronic disposal often happens in waves—during office relocations, technology refreshes, or departmental upgrades. This creates logistical challenges for proper handling and storage.
Data Security Risks: Business devices typically contain sensitive information. A single improperly disposed hard drive can create significant legal and reputational damage, with potential costs averaging $150 per compromised record according to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report.
Compliance Navigation: Understanding and adhering to Illinois e-waste regulations requires time and expertise many businesses don’t have internally.
Resource Limitations: Smaller Metro East businesses often lack dedicated sustainability personnel or established relationships with qualified e-waste processors.
Tracking and Reporting Gaps: Many organizations struggle to document their e-waste disposal for audit and compliance purposes, creating potential regulatory exposure.
The Business Case for Proper E-Waste Management
Implementing structured business e-waste management delivers multiple advantages beyond environmental benefits:
Financial Incentives
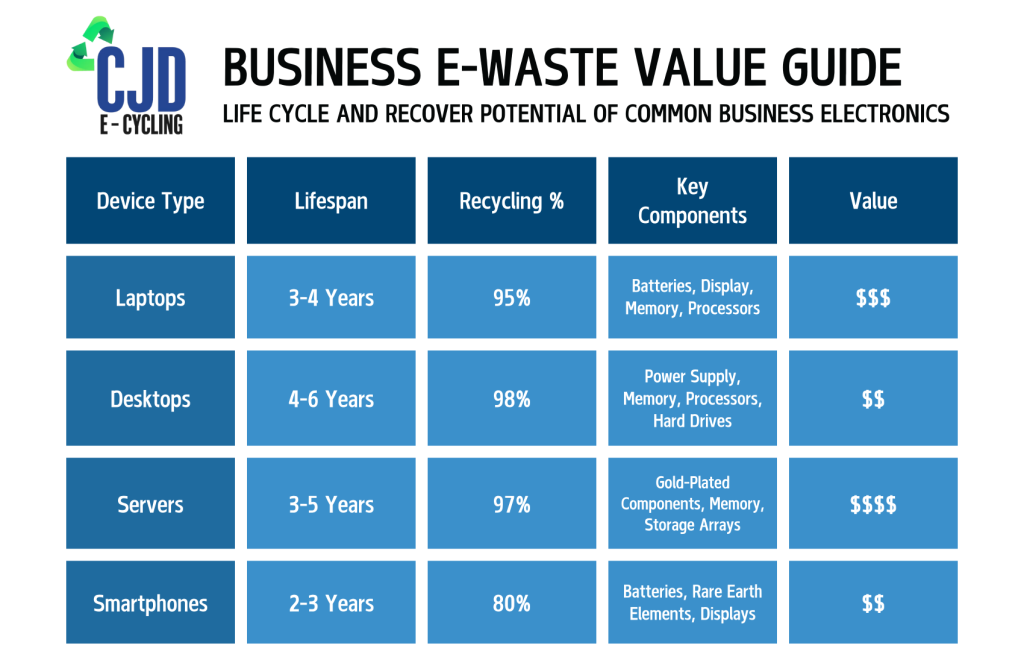
Asset Recovery Value: Many business electronics retain resale value even after their organizational usefulness ends. A properly managed IT asset disposition program can recover 15-20% of the original hardware value, offsetting replacement costs.
Tax Benefits: Donating functional but outdated equipment to qualified organizations may provide tax deductions for your business.
Avoided Disposal Costs: Proper planning prevents costly emergency disposal situations and potential fines for improper handling.
Risk Mitigation
Data Security Assurance: Professional data destruction services provide documentation that helps demonstrate due diligence in protecting sensitive information.
Regulatory Compliance: Formalized processes ensure adherence to Illinois Environmental Protection Agency requirements and federal regulations like HIPAA (for healthcare) or GLBA (for financial institutions).
Brand Enhancement
Demonstrable Sustainability: Proper business e-waste management provides measurable environmental impact metrics for sustainability reporting.
Competitive Differentiation: For B2B companies especially, documented sustainability practices increasingly influence procurement decisions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Business E-Waste Management Program
Step 1: Conduct an Electronic Asset Inventory
Begin by documenting all electronic equipment currently in use, including:
- Device types, models, and quantities
- Average replacement cycles
- Current end-of-life handling practices
- Potential sensitive data contained
This baseline assessment reveals the scale of your business e-waste challenge and identifies priority areas.
Step 2: Develop a Formal E-Waste Policy
Create a documented policy that outlines:
- Which items require specialized disposal
- Internal responsibilities for collection and processing
- Approved vendors for recycling and data destruction
- Documentation requirements for compliance
- Employee education requirements
Your policy should address both day-to-day disposal needs and larger equipment refresh projects.
Step 3: Establish Collection Infrastructure
Designate specific collection points within your facility featuring:
- Clearly labeled containers for different e-waste categories
- Secure storage for items containing sensitive data
- Sufficient capacity for normal operational volumes
- Appropriate access controls to prevent unauthorized removal
For larger Metro East businesses, consider implementing a departmental coordinator system to ensure consistent compliance across multiple teams.
Step 4: Implement Employee Education
Develop training materials that explain:
- What constitutes business e-waste
- Proper internal disposal procedures
- Data security responsibilities
- Environmental and business benefits of compliance
Consider incorporating e-waste guidelines into new employee onboarding and annual refresher training.
Step 5: Select an E-Waste Recycling Partner
Partner with a reputable e-waste recycler like CJD E-Cycling that provides:
- Documented chain-of-custody procedures
- Certified data destruction services
- Transparent processing practices
- Compliance documentation
- Convenient pickup options for Metro East businesses
Look for certifications like R2 (Responsible Recycling) or e-Stewards that verify adherence to rigorous environmental and data security standards.
Step 6: Establish Data Destruction Protocols
Create tiered data security procedures based on device type and sensitivity:
- Standard wiping for non-sensitive equipment
- Certified data destruction for storage media containing business information
- Physical destruction for highly sensitive data storage
Ensure your processes create documentation that could be used to demonstrate due diligence in the event of an audit.
Step 7: Implement Tracking and Documentation Systems
Maintain records of:
- Equipment disposed (types, quantities, dates)
- Data destruction certifications
- Recycling verification
- Weight or unit counts for sustainability reporting
Consider implementing asset tags and a simple database to track equipment from acquisition through disposal.
Special Considerations for Different Business Types
Small Businesses (1-50 employees)
Small Metro East businesses should focus on:
- Partnering with full-service e-waste recyclers to minimize internal resource requirements
- Scheduled quarterly collection events rather than continuous programs
- Simplified policies focused on compliance essentials
- Taking advantage of periodic community e-waste collection events
Mid-Size Companies (50-500 employees)
Medium-sized organizations benefit from:
- Designated e-waste coordinators within IT departments
- Regular scheduled pickups from recycling partners
- More comprehensive asset recovery programs
- Department-specific collection procedures
Enterprise Organizations (500+ employees)
Larger enterprises should implement:
- Integrated asset management systems tracking equipment from purchase to disposal
- Comprehensive value recovery programs
- Customized pickup schedules based on operational patterns
- Detailed sustainability metrics for corporate reporting
Industry-Specific Approaches
Healthcare: Emphasize HIPAA compliance in all disposal activities Financial Services: Implement enhanced chain-of-custody documentation Manufacturing: Focus on specialized equipment with electronic components Professional Services: Address distributed equipment across multiple locations
CJD E-Cycling’s Business E-Waste Solutions
As a family-owned electronics recycling company serving the Metro East and St. Louis areas, CJD E-Cycling offers specialized business e-waste management services:
Tailored Pickup Programs: Schedule regular pickups tailored to your business volume and schedule, eliminating transportation hassles.
Certified Data Destruction: Protect your business information with documented data destruction services that comply with industry standards.
Asset Value Recovery: Recover value from usable equipment to offset recycling costs or to reinvest in new technology.
Compliance Documentation: Receive verification of proper disposal for your regulatory compliance and sustainability reporting.
Comprehensive Processing: Feel confident knowing all materials are handled ethically, with hazardous components properly managed and valuable materials reclaimed.
Conclusion: Building Your Business E-Waste Success Story
Implementing a comprehensive business e-waste management program transforms an operational challenge into an opportunity for cost savings, risk reduction, and environmental leadership. For Metro East businesses, partnering with a local expert like CJD E-Cycling simplifies compliance while delivering tangible business benefits.
Begin by assessing your current electronic inventory and disposal practices, then develop a straightforward policy that addresses your specific business needs. With the right processes and partners in place, managing business e-waste becomes less of a burden and more of a competitive advantage.
Ready to transform your approach to business e-waste? Contact CJD E-Cycling today for a free consultation to identify the most effective solution for your organization’s needs.
Quick Facts: Business E-Waste by the Numbers
- 60%: Percentage of business e-waste that still ends up in improper disposal channels
- 98%: Percentage of business computers that can have components recycled or repurposed
- $11,000: Average annual savings for a 100-employee company implementing proper e-waste management
- 3-5 years: Typical useful lifespan of business computing equipment
- 20-30%: Potential recovery value from properly managed IT asset disposition