
In the rapidly evolving world of electronics, the challenge of managing e-waste has never been more pressing. According to the Global E-waste Monitor 2020, the world generated a staggering 53.6 million metric tons of e-waste in 2019, with projections reaching 74 million metric tons by 2030. Fortunately, cutting-edge technologies are emerging to tackle this issue head-on. Let’s explore five innovative e-waste recycling technologies that are transforming the industry in 2024, with insights on how they’re being implemented in the Metro East and St. Louis areas.
Comparison of Innovative E-Waste Recycling Technologies
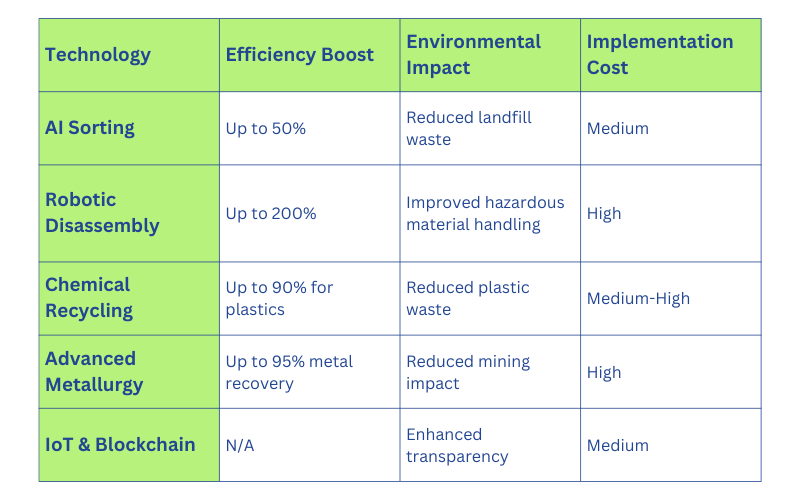
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Sorting and Identification
Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing the sorting process in e-waste recycling. Advanced AI algorithms, coupled with computer vision, can quickly and accurately identify different types of electronic components and materials.
Key Benefits:
- Increased sorting accuracy up to 99%
- Faster processing times, boosting efficiency by up to 50%
- Ability to identify and separate valuable rare earth elements
AI-powered sorting systems can distinguish between various types of plastics, metals, and other materials, ensuring more efficient recycling and recovery of valuable resources.
At CJD E-Cycling, we’re exploring AI-powered sorting solutions to enhance our electronic recycling services in the Metro East area.
2. Robotics for Disassembly and Hazardous Material Handling
Robotic systems are increasingly being employed to handle the disassembly of electronic devices and the management of hazardous materials.
Advantages:
- Improved worker safety by minimizing exposure to harmful substances
- Consistent and precise disassembly, increasing the recovery of reusable components
- 24/7 operation capability, enhancing overall recycling capacity
These robotic systems can delicately remove batteries, separate different components, and handle materials containing mercury or other toxic substances with precision and safety.
Our team at CJD E-Cycling is currently evaluating robotic systems to complement our data destruction services, ensuring even greater security and efficiency.
3. Chemical Recycling for Plastics
Innovative chemical recycling processes are addressing the challenge of recycling mixed and contaminated plastics found in electronic waste.
How it works:
- Plastics are broken down into their basic chemical components
- These components can then be used to create new, high-quality plastics
- Reduces the need for virgin plastic production
This technology allows for the recycling of plastics that were previously considered non-recyclable, significantly reducing the environmental impact of e-waste. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recognizes chemical recycling as a promising approach to plastic waste management.
4. Advanced Metallurgy Techniques for Precious Metal Recovery
New metallurgical processes are enhancing the recovery of precious metals like gold, silver, and palladium from electronic components.
[Insert Precious Metal Recovery Infographic]
Innovations include:
- Bioleaching: Using bacteria to extract metals from e-waste
- Electrochemical recovery: Employing electrical currents for precise metal separation
- Supercritical water oxidation: Breaking down hazardous organic compounds while recovering metals
These techniques not only increase the yield of valuable metals but also reduce the environmental impact of the recovery process. Research from the Journal of Cleaner Production highlights the potential of these advanced metallurgy techniques in e-waste management.
5. IoT and Blockchain for Tracking and Transparency
The Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain technology are being integrated into e-waste management systems to improve tracking and ensure transparency throughout the recycling process.
[Insert IoT and Blockchain Tracking Visualization]
Benefits:
- Real-time tracking of e-waste from collection to final recycling
- Enhanced accountability and reduced risk of illegal dumping
- Improved data collection for optimizing recycling processes
This technology allows consumers and businesses to verify that their e-waste is being handled responsibly, fostering trust in the recycling process. At CJD E-Cycling, we’re investigating how to incorporate these technologies into our IT asset disposal (ITAD) services.
The Future of E-Waste Recycling
[Insert Future of E-Waste Recycling Concept Art]
These innovative technologies are just the beginning. As we continue to generate more electronic waste, the recycling industry is responding with increasingly sophisticated solutions. At CJD E-Cycling, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these technological advancements to provide the most efficient and environmentally friendly e-waste recycling services possible in the Metro East and St. Louis areas.
By embracing these innovations, we can turn the challenge of e-waste into an opportunity for resource recovery and environmental protection. Together, we can work towards a future where electronic waste is not a burden, but a valuable resource in the circular economy.
Ready to recycle your e-waste using cutting-edge technologies? Contact CJD E-Cycling today and be part of the recycling revolution in the Metro East!
FAQs About Innovative E-Waste Recycling Technologies
- Q: How does AI improve e-waste recycling? A: AI enhances sorting accuracy, speeds up processing, and can identify valuable materials like rare earth elements more efficiently than traditional methods.
- Q: Are robotic disassembly systems safe? A: Yes, robotic systems improve safety by handling hazardous materials and reducing human exposure to potentially harmful substances in e-waste.
- Q: Can chemical recycling handle all types of plastics in e-waste? A: While not all plastics can be chemically recycled yet, this technology significantly increases the types of plastics that can be effectively recycled from e-waste.
- Q: How do advanced metallurgy techniques benefit the environment? A: These techniques increase the recovery of precious metals while reducing the need for environmentally damaging mining operations and minimizing waste.
- Q: How does blockchain technology ensure responsible e-waste recycling? A: Blockchain provides a transparent, tamper-proof record of the e-waste recycling process, allowing for better tracking and verification of responsible recycling practices.
